When doing website SEO I often get involved in various aspects of the website itself, either to advise or make changes to the website itself, or sometimes to recommend a website designer or hosting company, but also I occasionally delve into the dark world of DNS and Nameservers.
When it comes to owning a domain, there are many technical terms that can be overwhelming for beginners. One of those terms is “nameserver”, and having been asked more than once about this I thought it wise to document it, very simply for future such inquiries.
In this blog post, I will explain what a nameserver is, why it is important for the operation of your website and how it relates to the domain and hosting of your site.
Just to qualify this, I realise the below will be quite simplified, as I’m only documenting the required parts for a standard website domain owner, just for them to understand what the various names mean, and I do not pretend to be a networking or DNS expert (even though I’ve built and maintained many websites in the past) so I’m happy to be corrected, and I will update the article accordingly based on feedback received.
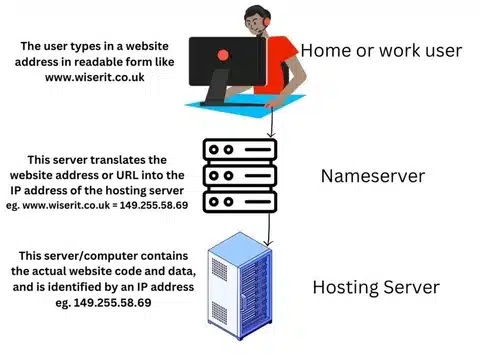
In simple terms, when a home or business user connects to a website, they will be directed to their websites nameserver which will use DNS records to translate the web domain into an IP address and therefore form the connection between the user’s browser and the remote website on a server within the web hosting company.
If that all sounds like a mouthful of gobbledegook, then let me try and explain what each of these elements means, and how each relates to the next.
What is a website domain?
A website domain also known as a Universal Resource Locator (URL) or Web Address is a unique address that identifies your website on the internet. It is the name that you type into a web browser to access your website, for example, www.wiserit.co.uk
A website domain is made up of two parts: the domain name and the domain extension.
The domain name is part of the website domain that comes before the dot (.) For example, in the domain name www.wiserit.co.uk, the domain name is “wiserit”. The domain name can be any combination of letters, numbers, and hyphens, and it is chosen by the owner of the website.
The domain extension is part of the website domain that comes after the dot (.) For example, in the domain name www.wiserit.co.uk, the domain extension is “.co.uk”. The domain extension can be any combination of letters, and it is usually used to indicate the purpose or location of the website. There are many different domain extensions available, including .co.uk, .com, .org, .net, .gov, .info, etc.
A website domain is very useful because it provides not only a unique identity for a website on the internet but also a meaningful set of readable letters or words, rather than a meaningless string of numbers (see IP address below). It allows users to find and access your website easily, and it can help to establish the credibility and professionalism of the website or help the user to identify where in the world your business is located.
Choosing a memorable and relevant domain name can help to improve the visibility and search engine ranking of a website. In Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) terms, having one or more of the keywords for the business can be a small help towards ranking the website for those keywords within the Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
To obtain a website domain, you need to register it with a domain registrar. There are many different domain registrars available, and the registration process typically involves choosing your domain name including the domain extension, checking to ensure this is not already registered, and providing contact and payment information. Once the registration process is complete, you own the rights to use the website domain for a specified period, usually one or more years at a time.
What is an IP Address?
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique numerical identifier assigned to each device that connects to the Internet.
It serves as a way for devices to communicate with each other over the internet, allowing data to be transmitted between them.
An IP address consists of four sets of numbers separated by periods, with each set ranging from 0 to 255, hence 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
There are two versions of IP addresses, IPv4 and IPv6, with IPv4 being the most commonly used, and probably the most familiar to most people.
The IP address can be static or dynamic, with static addresses being manually assigned and dynamic addresses being automatically assigned by a server. For example a website will have a fixed IP address unless it’s moved from one server to another, and large corporations tend to have one or more fixed IP. Whereas your home network supplied by your internet service provider would usually have a dynamic IP, and every time you reset your home router you may get a different IP address assigned to it.
What is a nameserver and how does it work?
In simple terms, a nameserver is a server or computer that translates domain names into IP addresses. Every website has an IP address, which as stated above, is a unique numerical identifier assigned to a specific device on the internet, for example, 149.255.58.69. However, IP addresses due to their structure are difficult for humans to remember and use. That’s where domain names come in because domain names are human-readable names that are easier to remember and use than IP addresses.
When you type a domain name into your web browser, your computer sends a request to a nameserver to find the IP address associated with that domain name. The nameserver then responds with the IP address, and your computer connects to the server hosting the website.
Nameservers are crucial for the functioning of the internet, they contain the DNS records without which, you would have to remember the IP address of every website you wanted to visit, which is simply not practical.
Each domain name has at least two nameservers associated with it. These nameservers are provided by the domain registrar or hosting provider that you used to register your domain. When you register a domain, you specify the nameservers that should be used for that domain.
When you make changes to your domain settings, such as changing the web hosting provider or email provider, you may need to update the nameservers for your domain. This is because the nameservers tell other devices on the internet where to find your website and other services associated with your domain.
In summary, nameservers are an essential part of the infrastructure that makes the Internet work. They translate human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses, which allows us to access websites and other online services. Make sure to keep your domain’s nameservers up-to-date to ensure that your website and other services remain accessible to users.
What does DNS stand for?
DNS stands for Domain Name System, and it is the system that is used to translate human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses.
The DNS system works by using a distributed network of servers to manage and store information about domain names and their corresponding IP addresses. Nameservers form part of this network by helping to store the DNS records that do this translation from domain names into IP addresses and thus help to pass the website visitor to the correct final destination online.
DNS is essential for the functioning of the internet, and it is used not only for accessing websites but also for many other online services, such as email, file sharing, and online gaming.
Every device that is connected to the internet, whether it is a computer, smartphone, or tablet, has an IP address that uniquely identifies it on the internet. Though not every one will be listed within the DNS, as some may not be accessible locations or live websites that need to be connected to by the public, whilst others may be uniquely connected via the IP address, and thus do not need a readable format or address by which to be referenced.
What is a hosting server?
A hosting server is a type of large powerful computer that is used to store website files and data that is published over the internet.
When you create a website, you need to store the files and data that make up the website on a server that has a direct and constant connection to the internet. A hosting server provides this functionality by allowing website owners to rent space on the server to store their website files and data.
When a user visits a website via their web browser, their computer sends a request to the hosting server associated with that domain. The hosting server then sends the website files and data back to the user’s computer, which allows the user to view the website in their browser.
There are many different types of hosting servers available, including shared hosting, virtual private servers (VPS), and dedicated servers.
- Shared web hosting is a type of hosting where multiple websites share a single server. This is the most common type of hosting, and it is usually the most affordable option for small websites or blogs with small amounts of data and low usage that are not mission-critical and don’t require high speeds.
- VPS (Virtual Private Server) hosting is a type of hosting where multiple virtual servers are created on a single physical server. This type of hosting offers more resources and control than shared hosting but since it is still somewhat shared is still more affordable than a dedicated server.
- Dedicated hosting is a type of hosting where an entire physical server is rented by a single website owner. This type of hosting offers the most resources and control but is also the most expensive option.
Hosting servers are typically managed by hosting providers, who are responsible for maintaining the servers, installing software updates, and providing technical support to website owners. Hosting providers offer a range of features and services, such as website builders, email hosting, and security features, to help website owners manage their websites.
How does any of this affect SEO?
So part of the best practice for SEO is to have a fast, reliable website for the best user experience.
If your web domain is short, meaningful and memorable it gives a company a great start in the journey, as it means visitors may be more likely to return to the website.
A good, reliable and fast web hosting company is also essential for not only the user experience, but also Google will rank your website based on the speed at which it operates, as if it’s too slow it will see that and rank faster sites above yours.
It goes without saying then that having DNS set up correctly on the NameServer is absolutely required, otherwise, your visitors are unlikely to ever find your website at all!
LOOKING FOR AN SEO CONSULTANT?
If you are looking for an SEO consultant to help your business call Wiser IT today on 07941 783434 or fill in the contact form